56. Invert Binary Tree
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.
Example 1:

Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
Example 2:
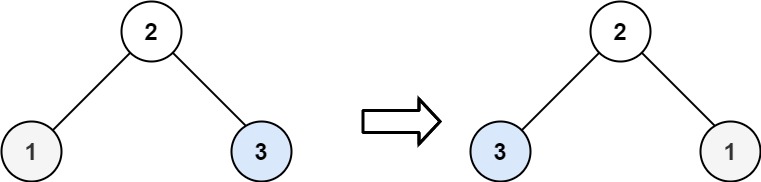
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: [2,3,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
return None
# Swap the left and right children
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
# Recursively invert the left and right subtrees
self.invertTree(root.left)
self.invertTree(root.right)
return root
Explanation
This problem can be solved elegantly using recursion.
Core Idea: To invert a binary tree, we need to swap the left and right children of every node in the tree.
Recursive Approach:
-
Base Case: If the
rootisNone(an empty tree or a null child), there's nothing to invert, so we returnNone. -
Recursive Step:
- Swap Children: For the current
rootnode, we swap itsleftandrightchildren. Python's tuple assignment makes this very concise:root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left. - Recurse on Subtrees: After swapping the children of the current node, we recursively call
invertTreeon the (now new)root.leftandroot.rightsubtrees. This ensures that the inversion process is applied to all nodes down to the leaves.
- Swap Children: For the current
-
Return Root: Finally, we return the
rootof the inverted tree.
Time and Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the binary tree. We visit each node exactly once.
- Space Complexity: O(H) in the worst case, where H is the height of the tree. This is due to the recursion stack. In a skewed tree, H can be N (O(N)), and in a balanced tree, H is log N (O(log N)).