10. Container With Most Water
Problem Statement
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
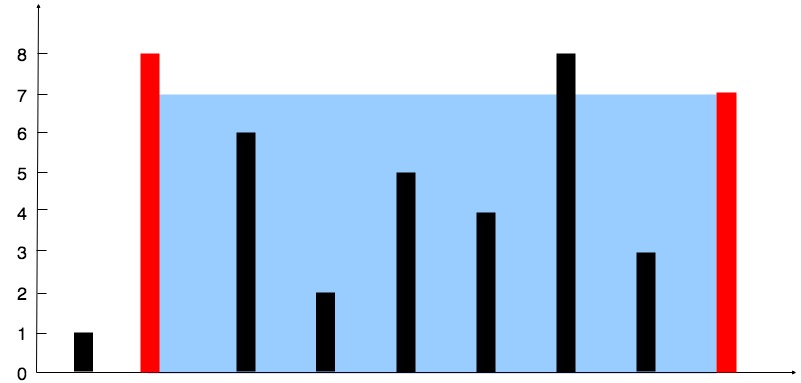
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1] Output: 1
Solution
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: list[int]) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(height) - 1
max_area = 0
while left < right:
# Calculate the area
h = min(height[left], height[right])
w = right - left
area = h * w
max_area = max(max_area, area)
# Move the pointer pointing to the shorter line
if height[left] < height[right]:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return max_area
Explanation
This problem can be solved efficiently using a two-pointer approach.
We initialize two pointers, left at the beginning of the array and right at the end.
The area of the container formed by these two lines is determined by the shorter of the two heights (as that's the water level) and the distance between the lines.
In each step, we calculate the area and update our max_area. Then, we need to decide which pointer to move. To maximize the area, we should try to increase the shorter height. Therefore, we move the pointer that points to the shorter of the two lines inward.
This process continues until the pointers meet. The time complexity is O(n) because we traverse the array once. The space complexity is O(1).