53. Add Two Numbers
Problem Statement
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit.
Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
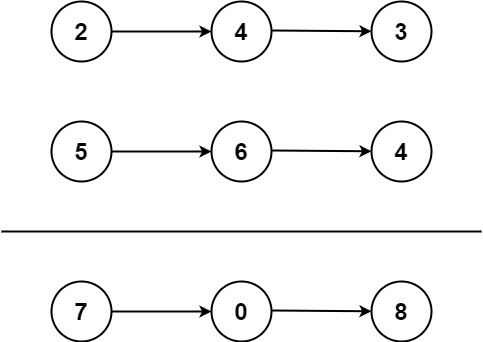
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Solution
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy_head = ListNode(0)
current = dummy_head
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry:
val1 = l1.val if l1 else 0
val2 = l2.val if l2 else 0
total_sum = val1 + val2 + carry
carry = total_sum // 10
digit = total_sum % 10
current.next = ListNode(digit)
current = current.next
if l1:
l1 = l1.next
if l2:
l2 = l2.next
return dummy_head.next
Explanation
This problem simulates the process of adding two numbers digit by digit, just like we do manually, but with the digits stored in reverse order in linked lists.
-
Dummy Head: We create a
dummy_headnode. This is a common practice in linked list problems to simplify the handling of the first node of the result list. We also use acurrentpointer, initially pointing todummy_head. -
carryVariable: We initialize acarryvariable to 0, which will store any carry-over from the sum of digits. -
Iteration: We iterate using a
whileloop as long as there are still digits inl1,l2, or there is acarryremaining.- Get Digit Values: In each iteration, we get the value of the current digit from
l1andl2. If a list has been exhausted, we treat its value as 0. - Calculate Sum and Carry: We calculate the
total_sumof the two digit values and thecarryfrom the previous step. - The new
carryistotal_sum // 10(integer division). - The
digitto be added to the result list istotal_sum % 10(the remainder). - Create New Node: We create a new
ListNodewith thisdigitand append it tocurrent.next. - Advance Pointers: We then advance
currentto the newly created node, and also advancel1andl2to their next nodes if they exist.
- Get Digit Values: In each iteration, we get the value of the current digit from
-
Return Result: After the loop finishes,
dummy_head.nextwill point to the head of the resulting linked list.
Time and Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(max(m, n)), where m and n are the lengths of
l1andl2respectively. We iterate through the longer of the two lists once. - Space Complexity: O(max(m, n)), as the length of the new linked list will be at most
max(m, n) + 1(for a potential final carry).